9 Chapter 8: Time Management and Goal Setting
“Time is more valuable than money. You can get more money, but you cannot get more time.”
-Jim Rohn
My favorite aspect of time is its equality. Regardless of our race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or age, all of us have the same amount of time in a day, week, month and year. Wealthy people cannot buy more time and poor people do not receive less time. A minute for a tall person is the same amount of time for a short person. An hour for a woman is the same amount of time for a man. Regardless of how many languages someone speaks, their sexual orientation, ethnicity, educational background, income or experience, we all have 365 days in a year. Some people will live longer than others, but when comparatively measuring how much time humans have with each other, we all have the same amount.
Time is a popular philosophical concept. You may have heard some of the following sayings:
- Time flies when you are having fun
- That is a waste of time
- Time is money
- We have all the time in the world
- That was an untimely death
- The time is right
- I’m having the time of my life
- Time heals all wounds
- We have some time to kill
What do the sayings mean to you?
Time is also how we keep track of when we’re supposed to be and where we’re supposed to be (work, home, class, meeting friends and family, etc.). Think about how many measures of time you have in your home (clocks, watches, cell phones, TVs, DVRs, computers, microwaves, ovens, thermostats, etc.). It is obvious time is important to us.
Time: A Limited and Precious Commodity
We cannot go back in time. If I used my time poorly last Wednesday, I can do nothing to get it back. Other commodities may allow for accumulating more or starting over, but time does not. We cannot “save” time nor earn more time.
“If you had a bank that credited your account each morning with $86,400, but carried no balance from day to day and allowed you to keep no cash in your account, and every evening cancelled whatever part of the amount you had failed to use during the day, what would you do? Draw out every cent, of course! Well, you have such a bank, and its name is time. Every morning it credits you with 86,400 seconds. Every night it writes off as lost whatever of these you have failed to invest to good purpose. It carries no balance; it allows no overdrafts. Each day it opens a new account with you. Each night it burns the record of the day. If you fail to use the day’s deposit, the loss is yours. There is no going back. There is no drawing against the morrow. You must live in the present – on today’s deposit. Invest it so as to get the utmost in health and happiness and success.”
– Anonymous
Technically, time cannot be managed, but we label it time management when we talk about how people use their time. We often bring up efficiency and effectiveness when discussing how people spend their time, but we cannot literally manage time because time cannot be managed. What we can do though, is find better ways to spend our time, allowing us to accomplish our most important tasks and spend time with the people most important to us. We can self-manage ourselves. This includes motivating oneself and setting and working towards your personal and academic goals.
Human babies do not come with instruction manuals. There is nothing to follow to know how we are supposed to spend our time. Most of us spend our time doing a combination of what interests us, what is important to us and what we feel we “have” to do.
What is your relationship with time? Are you usually early, right on time or late? Do you find yourself often saying, “I wish I had more time?” Are you satisfied with your relationship with time or would you like to change it? What are your cultural and family values related to time?

The Value of Time
It is also important to determine how much your time is worth to you. If someone were to negotiate for an hour of your time, how much would that be worth to you? We often equate time with money. Many of us work in positions where we are paid by the hour; this gives us some gauge of what we are worth to our employers. Some items we purchase because we think they are of good value for their price. Others we pass on. Are some hours of your day more important or more valuable than others? Why? Are you more productive in the morning or in the evening? Once people realize how valuable time is, they often go to great lengths to protect it because they understand its importance. How much would you pay for an additional hour in a day? What would you do with that time? Why?
What is the value of your time? How much is an hour of your time worth? If someone were to pay you $10 to do a job, how much time would that be worth? $20? $50?
How Do I Allocate My Time?
“Lack of direction, not lack of time is the problem. We all have 24 hour days.”
– Zig Ziglar
Most of us know there are 24 hours in a day, but when I ask students how many hours are in a week, many do not know the answer. There are 168 hours in a week (24 hours multiplied by seven days). I don’t believe that it is imperative that students know how many hours are in a week, but it helps when we start to look at how much time we have in a week, how we want to spend our time and how we actually spend our time.
One challenge for many students is the transition from the structure of high school to the structure of college. In high school, students spend a large portion of their time in class (approximately 30 hours in class per week), while full-time college students may spend only one-third of that time in class (approximately 12 hours in class per week). Further, college students are assigned much more homework than high school students. Think about how many times one of your high school teachers gave you something to read during class. In college, students are given more material to read with the expectation that it is done outside of class.
This can create challenges for students who are unable to set aside proper study time for each of their courses. Keep in mind for full-time students: your college educational day should not be shorter than your high school day.
Hourly Recommendations (per Week)
| Work Hours | Credits | Study Time | Total |
| 40 | 6 | 12 | 58 |
| 30 | 9 | 18 | 57 |
| 20 | 12 | 24 | 56 |
I use this table frequently in counseling appointments, classes and orientations. It’s a guide for students that provides an idea of how much time students spend with work and school, and what experts recommend for a specific amount of work hours that correlates with a specific number of credits. I like to ask students how they spend their week. Students always know their work hours and their class times. These are easy to place in a schedule or on a calendar because they are predetermined. But study time is the one area that consistently is left out of a student’s schedule. It takes initiative to include it in a student’s busy week and self-discipline to stick to it. Here’s a tip: Write your study time into your schedule or calendar. It’s important to do this because it’s easy to skip a study session or say to yourself, “I’ll do it later.” While there would likely be an immediate consequence if you do not show up for work, there is not one if you fail to study on Tuesday from 3pm-4pm. That consequence may take place later, if the studying is not made up.
It is widely suggested that students need to study approximately two hours for every hour that they spend in class in order to be successful. Thus, if I am taking a class that meets on Mondays and Wednesdays from 4pm-5:30pm (three hours per week), I would want to study outside of class six hours per week. This is designed as a guide and is not an exact science. You might need to spend more time than what is recommended if you are taking a subject you find challenging, have fallen behind in or if you are taking short-term classes. This would certainly be true if I were to take a physics class. Since I find learning physics difficult, I might have to spend three or four hours of study time for each hour of class instruction. You also might need to study more than what is recommended if you are looking to achieve better grades. Conversely, you might need to spend less time if the subject comes easy to you or if there is not a lot of assigned homework.
Keep in mind that 20 hours of work per week is the maximum recommended for full-time students taking 12 semester units in a term. For students working full-time (40 hours a week), no more than six credits is recommended. The total is also a very important category. Students often start to see difficulty when their total number of hours between work and school exceeds 60 per week. The amount of sleep decreases, stress increases, grades suffer, job performance decreases and students are often unhappy.
How do you spend your 168 hours in a week?
- Child Care
- Class
- Community Service / Volunteer
- Commuting / Transportation
- Eating / Food Preparation
- Exercise
- Family
- Friends
- Household / Child Care Duties
- Internet / Social Media / Phone / Texting
- Party
- Recreation / Leisure
- Relationship
- Sleeping
- Spirituality / Prayer / Meditation
- Study
- Video Games
- Watching TV or Movies, Netflix, Youtube
- Work / Career
There is also the time it takes for college students to adjust to college culture, college terminology, and college policies. Students may need to learn or relearn how to learn and some students may need to learn what they need to know. What a student in their first college semester needs to know may be different than what a student in their last college semester needs to know. First semester students may be learning where classrooms are, building hours and locations for college resources, and expectations of college students. Students in their last semester may be learning about applying for their degree, how to confirm they have all of their requirements completed for their goal, and commencement information. Whatever it is students may need to learn, it takes time.
Fixed Time vs. Free Time
Sometimes it helps to take a look at your time and divide it into two areas: fixed time and free time. Fixed time is time that you have committed to a certain area. It might be school, work, religion, recreation or family. There is no right or wrong to fixed time and everyone’s is different. Some people will naturally have more fixed time than others. Free time is just that—it is free. It can be used however you want to use it; it’s time you have available for activities you enjoy. Someone might work 9am-2pm, then have class 3pm-4:30pm, then have dinner with family 5pm-6pm, study 6pm-7pm and then have free time from 7pm-9pm. Take a look at a typical week for yourself. How much fixed time do you have? How much free time? How much fixed and free time would you like to have?
Identifying, Organizing and Prioritizing Goals
The universal challenge of time is that there are more things that we want to do and not enough time to do them.
I talk to students frequently who have aspirations, dreams, goals and things they want to accomplish. Similarly, I ask students to list their interests at the beginning of each of my classes and there is never a shortage of items. But I often talk to students who are discouraged by the length of time it is taking them to complete a goal (completing their education, reaching their career goal, buying a home, getting married, etc.). And every semester there are students that drop classes because they have taken on too much or they are unable to keep up with their class work because they have other commitments and interests. There is nothing wrong with other commitments or interests. On the contrary, they may bring joy and fulfillment, but do they get in the way of your educational goal(s)? For instance, if you were to drop a class because you required surgery, needed to take care of a sick family member or your boss increased your work hours, those may be important and valid reasons to do so. If you were to drop a class because you wanted to binge watch a Netflix series, or spend more time on TikTok, Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram, you may have more difficulty justifying that decision, but it is still your decision to make. Sometimes students do not realize the power they have over the decisions they make and how those decisions can affect their ability to accomplish the goals they set for themselves.
I am no exception. I have a long list of things that I want to accomplish today, tomorrow, next week, next month, next year and in my lifetime. I have many more things on my list to complete than the time that I will be alive.
Identifying Goals
Recently, there has been a lot of attention given to the importance of college students identifying their educational objective and their major as soon as possible. Some high schools are working with students to identify these goals earlier. If you are interested in career identification, you may wish to look into a career decision making course offered by College of DuPage, COLLG 1105, Career Development. You may also wish to make an appointment with a counselor, visit Career Services and/or research potential career opportunities.
Goal identification is a way to allow us to keep track of what we would like to accomplish as well as a mechanism to measure how successful we are at achieving our goals.
How To Start Reaching Your Goals

Without goals, we aren’t sure what we are trying to accomplish, and there is little way of knowing if we are accomplishing anything. If you already have a goal-setting plan that works well for you, keep it. If you don’t have goals, or have difficulty working towards them, I encourage you to try this.
Make a list of all the things you want to accomplish for the next day. Here is a sample to do list:
- Go to grocery store
- Go to class
- Pay bills
- Exercise
- Social media
- Study
- Eat lunch with friend
- Work
- Watch TV
- Text friends
Your list may be similar to this one or it may be completely different. It is yours, so you can make it however you want. Do not be concerned about the length of your list or the number of items on it.
“Obstacles are things a person sees when he takes his eyes off his goal.”
– E. Joseph Cossman
You now have the framework for what you want to accomplish the next day. Hang on to that list. We will use it again.
Now take a look at the upcoming week, the next month and the next year. Make a list of what you would like to accomplish in each of those time frames. If you want to study abroad, visit a new city of state for leisure, or get a bachelor’s degree, write it down. Pay attention to detail. The more detail within your goals the better. Ask yourself this question: what is necessary to complete your goals?

GOAL Setting
With those lists completed, now lets take into consideration how the best goals are created. Commonly called “SMART” goals, it is often helpful to apply criteria to your goals. SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Timely. Perform a web search on the Internet to find out more about “SMART” goals. Are your goals SMART goals? For example, a general goal would be, “Achieve an ‘A’ in my anatomy class.” But a more specific, measurable, and timely goal would say, “I will schedule and study for one hour each day at the library from 2pm-3pm for my anatomy class in order to achieve an ‘A’ and help me gain admission to nursing school.” Whether goals are attainable or realistic may vary from person to person.
Now revise your lists for the things you want to accomplish in the next week, month and year by applying the SMART goal techniques. The best goals are usually created over time and through the process of more than one attempt, so spend some time completing this. Do not expect to have “perfect” goals on your first attempt. Also, keep in mind that your goals do not have to be set in stone. They can change. And since over time things will change around you, your goals should also change.
Another important aspect of goal setting is accountability. Someone could have great intentions and set up SMART goals for all of the things they want to accomplish. But if they don’t work towards those goals and complete them, they likely won’t be successful. It is easy to see if we are accountable in short-term goals. Take the daily to-do list for example. How many of the things that you set out to accomplish, did you accomplish? How many were the most important things on that list? Were you satisfied? Were you successful? Did you learn anything for future planning or self management? Would you do anything differently? The answers to these questions help determine accountability.
Long-term goals are more difficult to create and it is more challenging for us to stay accountable. Think of New Year’s Resolutions. Gyms are packed and mass dieting begins in January. By March, many gyms are empty and diets have failed. Why? Because it is easier to crash diet and exercise regularly for short periods of time than it is to make long-term lifestyle and habitual changes.
Now that you have evaluated your goals, you can begin to set goals for the semester ahead. One common tool for effective goal setting is developing SMART goals. These goals are:

Specific: Your goal will clearly define what you are going to accomplish. You will ask and answer the What and Why of your goal.
Measurable: You will identify criteria for measuring progress toward the attainment of each goal you set. This will be the definition of How you will attain your goal.
- How will you know when the result that you want has been achieved?
- How will you verify your achievement/performance of this goal?
Attainable: Is it possible for you to achieve your desired goal? Can you see a path to your accomplishment? You are the Who in this goal setting process. It is your positive attitude that will allow you to draw on your current strengths and develop new ones as you meet your goal.
Relevant: Realistic goals must represent an objective toward which you are willing to work and which are relevant to you. You need to identify Where this goal will take you. A goal can be both high and realistic; you are the only one who can decide just how high your goal should be. Just be sure that each of your goals represents substantial progress.
Time Bound: You need to create a sense of personal urgency by setting times for each step along the way. Knowing When you have to accomplish a task keeps to on track and accountable. What needs to be done by when? Be timely! [1][2]
Consider an example. I could say that my goal is to become a better runner. This goal is undefined, and I will not be able to tell if I have achieved it. A SMART goal would be, “I will complete a ten kilometer run in under one hour by the end of June after training with my running group twice weekly”. Note that this goal is time-bound, and includes specific and measurable criteria that help me to know if I have successfully achieved it.
Try it!
Begin to set your learning goals for this semester. Choose one goal, and use the SMART goal system to check that your goal is relevant and achievable. Click here to download a printable worksheet for this activity.
| Specific
|
|
| Measurable
|
|
| Attainable
|
|
| Relevant
|
|
| Time-bound
|
Extend Your Learning
Goal setting can be challenging, but clearly identifying where you want to go on your learning journey and how you intend to get there will help you in the long run.
- Learn more about the importance of goals and continue your practice of goals setting by using this SMART goals template
Organizing Goals
Place all of your goals, plans, projects and ideas in one place. Why? It prevents confusion. We often have more than one thing going on at a time and it may be easy to become distracted and lose sight of one or more of our goals if we cannot easily access them. Create a goal notebook, goal poster, goal computer file—organize it any way you want—just make sure it is organized and that your goals stay in one place.
Use Technology to your Advantage
Software and apps are now available to help with organization and productivity. Check out Evernote, One Note, or Stickies.
Break Goals into Small Steps

I ask this question of students in my classes: If we decided today that our goal was to run a marathon and then went out tomorrow and tried to run one, what would happen? Students respond with: (jokingly) “I would die,” or “I couldn’t do it.” How come? Because we might need training, running shoes, support, knowledge, experience and confidence—often this cannot be done overnight. An academic goal might be obtaining an A grade on a mid-term essay for a writing class. Small steps might include getting started, planning time for smaller tasks, researching, writing a draft, visiting a writing support service, having a friend proofread, revising. Instead of giving up and thinking it’s impossible because the task is too big for which to prepare, it’s important to develop smaller steps or tasks that can be started and worked on immediately. Once all of the small steps are completed, you’ll be on your way to accomplishing your big goals.
What steps would you need to complete the following big goals?
- Buying a house
- Finding a long term partner
- Attaining a bachelor’s degree
- Attaining an associate’s degree
Prioritizing Goals
Why is it important to prioritize? Let’s look back at the sample list. If I spent all my time completing the first seven things on the list, but the last three were the most important, then I would not have prioritized very well.
It would have been better to prioritize the list after creating it and then work on the items that are most important first. You might be surprised at how many students fail to prioritize.
After prioritizing, the sample list now looks like this:
- Go to class
- Work
- Study
- Pay bills
- Exercise
- Eat lunch with friend
- Go to grocery store
- Text friends
- Social media
- Watch TV
One way to prioritize is to give each task a value. A = Task related to goals; B = Important—Have to do; C = Could postpone. Then, map out your day so that with the time available to you, work on your A goals first. You’ll now see below our list has the ABC labels. You will also notice a few items have changed positions based on their label. Keep in mind that different people will label things different ways because we all have different goals and different things that are important to us. There is no right or wrong here, but it is paramount to know what is important to you, and to know how you will spend the majority of your time with the things that are the most important to you.
A Go to class
A Study
A Exercise
B Work
B Pay bills
B Go to grocery store
C Eat lunch with friend
C Text friends
C Social media
C Watch TV
Do the Most Important Things First

You do not have to be a scientist to realize that spending your time on “C” tasks instead of “A” tasks won’t allow you to complete your goals. The easiest things to do and the ones that take the least amount of time are often what people do first. Checking Facebook or texting might only take a few minutes but doing it prior to studying means we’re spending time with a “C” activity before an “A” activity.
People like to check things off that they have done. It feels good. But don’t confuse productivity with accomplishment of tasks that aren’t important. You could have a long list of things that you completed, but if they aren’t important to you, it probably wasn’t the best use of your time.
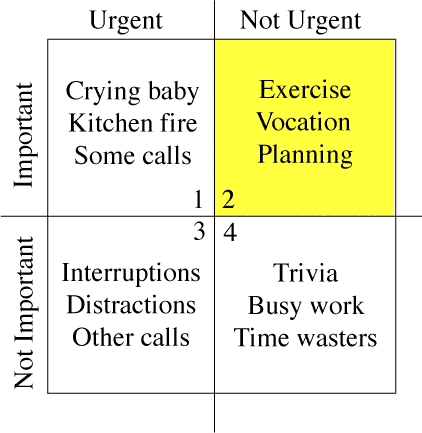
Perform an internet search for “Time Management Matrix Images.” The matrix shows how to categorize your tasks and will help prioritize your goals, tasks, and assignments. Take a look at the matrix and quadrants and identify which quadrant your activities would fall into.
Quadrant I (The quadrant of necessity)-Important and Urgent:
Only crisis activities should be here. If you have included exams and papers here, you are probably not allowing yourself enough time to fully prepare. If you continue at this pace you could burn out!
Quadrant II (The quadrant of quality and personal leadership)-Important and Not Urgent:
This is where you define your priorities. What’s important in your life? What will keep you balanced? For example, you may know that good nutrition, sleep, recreation and maintaining healthy social relationships are important but do you consciously make time for them in your daily or weekly routine? This may be where school fits. Where would time for class, homework, study time, required reading, preparing for exams fit in your overall priorities? Quadrant II includes your “A” goals. Managing your life and the lifestyle will help you manage your time.
Quadrant III (The quadrant of deception)-Not Important and Urgent:
While you may feel that activities, such as texting, need your attention right away, too much time spent on Quadrant III activities can seriously reduce valuable study time. This may leave you feeling pulled in too many directions at once.
Quadrant IV (The quadrant of waste)-Not Important and Not Urgent:
Quadrants three and four include your “C” goals. If you’re spending many hours on Quadrant IV activities, you’re either having a great deal of fun or spending a lot of time procrastinating! Remember, the objective is balance. You may notice I placed social media and texting into this category. You could make a case that social media, texting, Netflix, and Youtube are important, but how often are they urgent? Ultimately, it is up to you to decide what is important and urgent for yourself, but for the context of this textbook, your classes, assignments, preparation, and studying should almost universally be more urgent and important than social media and texting.
Here is an adapted version of the matrix, with an emphasis on quadrant II.
Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy, or one’s sense of being able to achieve goals, is an essential ingredient in a learner’s ability to succeed. Thoughts and feelings on this topic, which stem from one’s beliefs contribute to more, or less, success.
A key element of self-efficacy is the concept of locus of control. As the definition indicates, the locus, or place, of control is usually either internal or external, but sometimes it is both.
Obviously if a person believes that he/she is in control of situations and outcomes (an internal locus) achieving goals is more likely. If a person believes he/she is controlled by external forces, achieving goals is less likely. But everyone experiences both internal and external forces for various reasons. For example, choosing to do the right thing on the job is based on the external control of workplace rules. Yet, one might apply for the job based on one’s internal belief that he/she can succeed. And both internal and external loci of control are in operation when one chooses to do the right thing at any time based on one’s beliefs.
For a more detailed explanation and the relationship of self-efficacy to locus of control, complete this exercise.
EXERCISE 8-1
- List three attitudes and/or perspectives that a person with a primarily internal locus of control might have that will help him/her succeed in life, and why.
- List three attitudes and/or perspectives that a person with a primarily external locus of control might have that might hinder his/her success, and why.
- List three instances where both internal and external loci of control help a person, and why.
A chart might help you organize your response.
INTERNAL EXTERNAL BOTH
Conclusion
Managing time well comes down to two things. One is identifying (and then prioritizing) goals and the other is having the discipline to be able to work towards accomplishing them. We all have the same amount of time in a day, week, month and year, yet some people are able to accomplish more than others. Why is this? Often, it is because they are able to set goals, prioritize them and then work on them relentlessly and effectively until they are complete.
Licenses and Attributions:
CC licensed content, Original:
- Hop to It! by Maeko Gabrielle Ocampo. License: CC BY: Attribution No Derivatives.
- Setting Intentions by Shilo Vix. License: CC BY: Attribution.
Content previously copyrighted, published in Blueprint for Success in College: Indispensable Study Skills and Time Management Strategies (by Dave Dillon), now licensed as CC BY.
Roadmap graphics used with permission, courtesy of Greg Stoup, Rob Johnstone, and Priyadarshini Chaplot of The RP Group.
All rights reserved content:
Pausch, Randy. “Randy Pausch Lecture: Time Management.” YouTube, uploaded by Carnegie Mellon University, 6 Feb. 2008. Located at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oTugjssqOT0 License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
Fleming, Kevin and Marsh Brian Y. “Success in the New Economy”. Vimeo, uploaded by Citrus College, 2017. Located at: https://vimeo.com/67277269 License: All Rights Reserved.

