1.8 Safety Concepts
Safety: A Basic Need
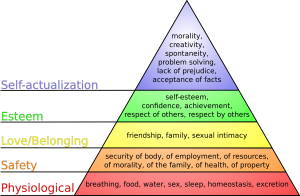
Safety is a basic foundational human need and always receives priority in patient care. Nurses typically use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to prioritize urgent patient needs, with the bottom two rows of the pyramid receiving top priority. See Figure 1.8 for an image of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Safety is intertwined with basic physiological needs.
Consider the following scenario: You are driving back from a relaxing weekend at the lake and come upon a fiery car crash. You run over to the car to help anyone inside. When you get to the scene, you notice that the lone person in the car is not breathing. Your first priority is not to initiate rescue breathing inside the burning car, but to move the person to a safe place where you can safely provide CPR.
In nursing, the concept of patient safety is central to everything we do in all health care settings. As a nurse, you play a critical role in promoting patient safety while providing care. You also teach patients and their caregivers how to prevent injuries and remain safe in their homes and in the community. Safe patient care also includes measures to keep you safe in the health care environment; if you become ill or injured, you will not be able to effectively care for others.
Safe patient care is a commitment to providing the best possible care to every patient and their caregivers in every moment of every day. Patients come to health care facilities expecting to be kept safe while they are treated for illnesses and injuries.
Attribution
This section contains material taken from Nursing Fundamentals 2e by Chippewa Valley Technical College and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Lice

