13.3 Overview of Mental Health and Mental Status
Mental Health
Mental health is the ability to adjust to changes and the stressors of life by using positive coping mechanisms. Mental health incorporates emotions, thoughts, and feelings; it includes the ability to solve problems, overcome difficulties, maintain social bonds, understand the world around us, and make healthy choices. Therefore, mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being.
Mental Illness
Mental illness is a disorder that prevents a person from coping with everyday life and requires long-term treatment. The disorder/illness affects how the person thinks, feels, behaves, and interacts with others. These changes in thinking, feeling, and behaving, any one or all three, can cause the individual emotional distress and alter the manner in which the individual functions. Mental illness, especially depression, increases the risk for many types of physical illness, especially chronic illness, e.g., diabetes mellitus II and coronary heart disease. The reverse is also true: chronic illnesses can potentiate mental illnesses. It is possible to have imperfect mental health without a mental illness, and it is also possible to have good mental health while having a diagnosis of a mental illness/psychiatric condition.
It is also possible to have different types of mental illnesses or disorders at the same time or at different times. Mental illness can be short-term, episodic, or long-term.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “mental illnesses are among the most common health conditions in the United States” (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2018).
Statistics
- 50% of individuals will have a mental status illness/disorder in their lifetime.
- Every year, 1 in 5 people will demonstrate signs of mental illness.
- At some point in their lives, 1 in 5 children will experience “debilitating mental illness” (Merikangas & Burstein 2010).
- Severe mental illness including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or major depression is suffered by 1 in 25 Americans.
Risk factors
Factors that can contribute to mental illness include:
- Early life trauma.
- Chronic diseases.
- Individual biological data, e.g., genetic makeup.
- Social isolation.
- Lack of social support.
- Use of illicit drugs and alcohol.
- Earlier onset of puberty.
- There may be a mismatch between a child’s appearance and the way she acts and thinks.
- For girls, earlier onset of puberty is associated with depression, substance use, eating disorders, disruptive behavior disorders, and early sexual behavior (Graber, 2013).
- Early-maturing girls demonstrate more anxiety and less confidence in their relationships with family and friends, and they compare themselves more negatively to their peers (Weir, 2016).
- For girls, the emphasis on physical attractiveness and sexuality is emphasized at puberty and they may lack effective coping strategies to deal with the attention they may receive (https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-lifespandevelopment/chapter/sexual-development/).
Two conditions that increase the risk for mental illness are addiction and abuse. Knowing how to assess a patient with addiction or correlating assessment findings with abuse can be life-saving.
Additional Reading
Assessing Mental Health in Vulnerable Adolescents
Suicide prevention tool based on CDC guidance.
Mental Status
Mental status is defined as a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s intellectual capacity, emotional state, and mental health. Mental status is assessed by the observations of the health care provider and direct one-to-one interviews. A mental status assessment observes mood, behavior, orientation, judgment, memory, problem-solving ability, ability to function in society, and contact with reality.
Assessment of Mental Status
Assessment of mental status may not occur routinely. In the hospital setting, the nurse completes a full mental status assessment on admission and any time during the individual’s hospital stay to establish if a change in mental state has occurred. Portions of the mental health assessment will be routinely assessed by nurses in almost all health care settings, because the patient’s mental health state is an integral aspect of the patient’s overall health status.
Steps:
1. Introduction
Introduce yourself to the patient and explain why and how the mental status exam will be completed. Ensure that the environment is clean, quiet, and non-threatening.
2. Patient Observation
Inspect the patient for the following:
- General appearance
- Behavior
- Thought process and content
- Affect
- Impulse control
- Insight
- Cognitive functioning
- Intelligence
- Reality testing
- Suicidal or homicidal ideation
- Judgment
Utilize what is seen and heard to direct the conversation to gather as much data as possible.
3. Document assessed data
Include primary language; demographics; education; mental, physical, and social functionality; support system; current problem; past medical, physical, and psychiatric histories; past life trauma; mood; emotions; nutrition; sleep; sexuality; thinking; perceptions (hallucinations); orientation; cognition and memory; and finally, all data obtained through observing all topics listed above.
4. Assessing Mental Status
https://wtcs.pressbooks.pub/nursingskills/chapter/6-4-assessing-mental-status/embed/#?secret=1r0N8Whbtc#?secret=GHfyavLGBi
The Mental Status Exam[1]
The Mini-Mental State Examination[2]:
This tool is widely used to assess cognitive impairment in several settings including inpatient, research, and community settings
The video below describes each section of the mental status exam.
Video: How to Conduct a Mental Status Exam by The Enlightened RN.
The standard format for documenting the Mental Status Examination varies a little, but as long as all areas are covered the exact order is not crucial.
Format for documenting the Mental State Examination:
- Appearance and Behavior
- Speech
- Mood
- Subjective
- Objective
- Risk
- Thoughts
- Form
- Content
- Beliefs—Overvalued or Delusional
- Perceptions
- Cognition
- Insight
Citation and Attribution
Learning about Mental Health, CDC. Reviewed January 26, 2018, Retrieved July 29, 2021 https://www.cdc.gov/mentalhealth/learn/index.htm
AAP. https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Mental-Health/Documents/MH_ScreeningChart.pdf
Working with People who are Mentally Ill https://milnepublishing.geneseo.edu/home-health-aide/chapter/working-with-people-who-are-mentally-ill/
The difference between mental health and illness https://insidemypurse.co.za/2019/10/31/the-difference-between-mental-health-and-illness/?gclid=CjwKCAjw87SHBhBiEiwAukSeUbg3uUiupghg0cWddctRZDvIlui8L5w5OcP5xh8KAE8Z530doBVDBBoChAAQAvD_BwE
Emotional Health and Mental/Emotional Disorders https://courses.lumenlearning.com/diseaseprevention/chapter/emotional-health-and-mentalemotional-disorders/
Mental Status https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/mental+status
Mental Status exam https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RdmG739KFF8
How to Conduct a Mental Status Exam https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2fOvfV3RDXc
How to do the Mental Status Exam | Merck Manual Professional Version https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=14s9jMf4vR8
Mental Health https://www.cdc.gov/mentalhealth/learn/index.htm
The brain and mental health. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pov3X-teO24
The Mental Status Examination https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK320/
The Mental Status Exam by Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mental_status_examination
Enoch MA, Goldman D. Problem drinking and alcoholism: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2002 Feb 1;65(3):441-8. PMID: 11858627.
Rayan, A., Assessment and Management of Patients With Drug Abuse: Nurses Should be Involved. Journal of Addiction and Dependence 2017 pg. 01-04 https://doi.org/10.15436/2471-061X-17-037 Retrieved July 28, 2021. https://www.ommegaonline.org/article-details/Assessment-and-Management-of-Patients-With-Drug-Abuse-Nurses-Should-be-Involved/1271
MR, King KC, Jordan GA, et al. Domestic Violence. [Updated 2021 Apr 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499891/
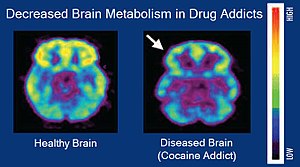
Decreased Brain Metabolism in Drug Addicts PET scan images showing brain metabolism in those with addictions vs controls. Addiction disrupts the normal, healthy functioning of the brain. Created February 14, 2018 Public domain Retrieved July 28, 2021, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Addiction#/media/File:Brain_metabolism_and_drug_addiction.jpg
Suicide prevention Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia edited at 03:08 July 9, 2021 Retrieved July 29, 2021. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suicide_prevention
Lally M., and Valentine-French, S. Lifespan Development. Sexual Development https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-lifespandevelopment/chapter/sexual-development/

